Tackling Tuberculosis: Understanding the Silent Threat
Tuberculosis (TB) stands as a persistent and formidable adversary.
Despite significant progress in prevention and treatment, TB continues to exact a heavy toll on individuals and communities worldwide.
Understanding the complexities of TB is essential for raising awareness, fostering early detection, and advancing efforts towards eradication
Tackling Tuberculosis: Understanding the Silent Threat
Tuberculosis (TB) stands as a persistent and formidable adversary. Despite significant progress in prevention and treatment, TB continues to exact a heavy toll on individuals and communities worldwide. Understanding the complexities of TB is essential for raising awareness, fostering early detection, and advancing efforts towards eradication.
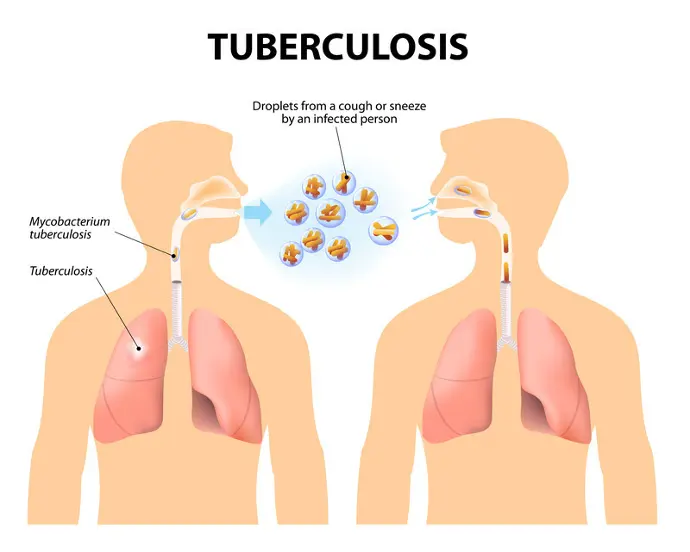
The Silent Spread:
TB often lurks silently within communities, with individuals unknowingly harboring the bacteria. Latent TB infection occurs when the immune system walls off the bacteria, preventing it from causing active disease. However, latent TB can progress to active TB disease if the immune system weakens, leading to symptoms and transmission to others.
Signs and Symptoms:
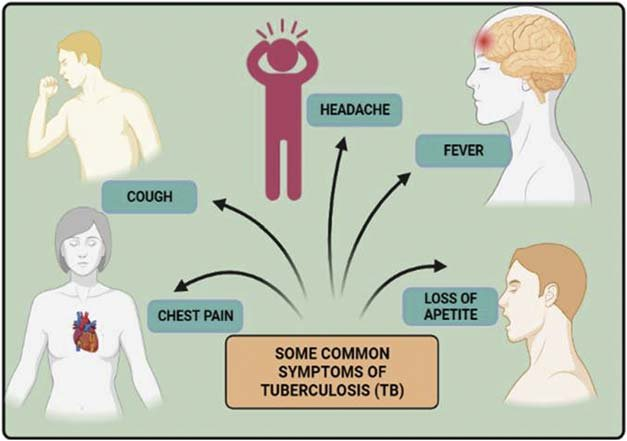
The symptoms of TB can vary depending on the site of infection but commonly include:
- Persistent cough lasting more than three weeks
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood or sputum
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Unintentional weight loss
Diagnosis and Detection
Diagnosing TB requires a multifaceted approach, including:
- Tuberculin Skin Test (TST) or Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs) to detect latent TB infection.
- Chest X-rays and sputum tests to diagnose active TB disease.
- Molecular diagnostic tests, such as GeneXpert MTB/RIF, for rapid and accurate detection of TB and drug resistance
Treatment and Prevention:
Treating TB requires a combination of antibiotics taken for an extended period, typically six to nine months for drug-susceptible TB.
Drug-resistant TB may necessitate more prolonged and complex treatment regimens.
Prevention strategies include:
Infection Control Measures
Implementing infection control measures in healthcare settings and congregate settings can reduce TB transmission.
Addressing Social Determinants:
Addressing poverty, improving housing conditions, and promoting access to healthcare are crucial for TB control.

Vaccination
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine offers partial protection against severe forms of TB, such as TB meningitis and disseminated TB in children.